Aromatization technology is the reaction of naphtha or liquefied gas under the action of catalyst, such as isomerization, cyclizing, dehydrogenation, cracking and polymerization, to produce mixed aromatic hydrocarbons or high octane blending components containing benzene, toluene and xylene.
Naphtha is mainly used as raw material for catalytic reforming or cracking of ethylene. For some small and medium-sized refineries and the refinery which on the marginal area or some oil stabilization plant of oil field, it is difficult for virgin naphtha to be used as raw material for catalytic reforming or cracking of ethylene, if directly with other gasoline blend ,the octane number is too low, will affect the economic value of the product. Therefore, this part of the resources can use naphtha aromization technology to produce high octane gasoline or aromatics, improve the economic value of naphtha.
1,Adaptable raw material
Naphtha or liquefied gas
2, Physicochemical properties of catalysts
Name | Analysis result |
Appearance | Gray cylindrical solid |
Bulk density g/m3 | 0.7-0.8 |
Diameter Ф mm | 2.5±0.2 |
Crushing strength N/cm | ≥80 |
Na2O | ≤0.10 |
3, Process conditions
Item | Index |
Reaction temperature ℃ | 300-420 |
Reaction pressure MPa(g) | 0.5-1.5 |
Mass S V,h-1 | 0.2-0.5 |
4,Technical flow diagram
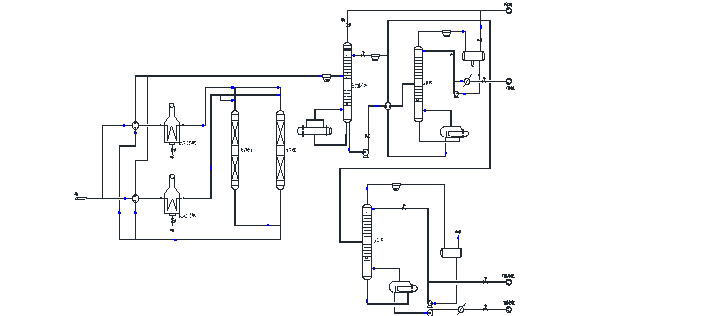
5,Process characteristics
Adopt high pressure method, omit rich gas compressor;the regeneration method adopts wet regeneration method, which saves nitrogen compressor and investment cost.